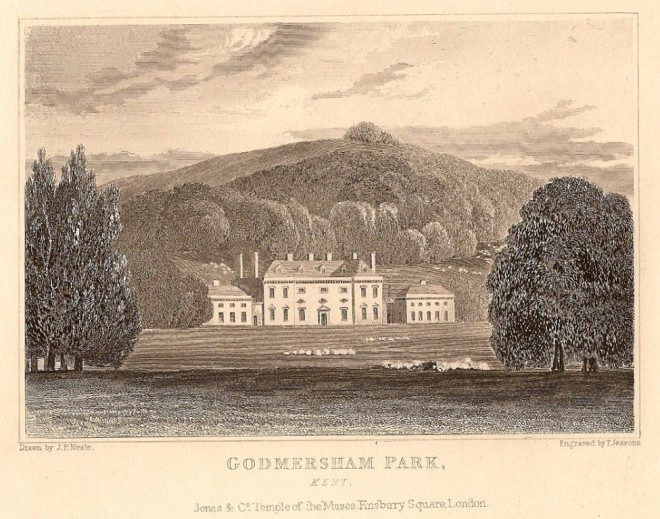
 Enquiring Readers: Today I welcome Austen scholar Hazel Jones in an interview about her newest book The Other Knight Boys: Jane Austen’s Dispossessed Nephews. If you have been following my blog Reading with Austen: Returning the Lost Sheep of Godmersham, you have seen the several posts on the diaries of Charles Bridges Knight, i.e all the excerpts that Hazel shared with me of Charles’ references to his reading in the library at Godmersham Park, home to his father, and Jane Austen’s brother, Edward Austen Knight [see below for links to these posts]. Hazel has been researching not only the life of Charles, but also the lives of the five other sons of Edward [all six in order are: Edward, George, Henry, William, Charles, and John]. Her recently published book just flows with tales of their childhood into manhood adventures. I highly recommend it, many of the stories worthy of an Austen novel!
Enquiring Readers: Today I welcome Austen scholar Hazel Jones in an interview about her newest book The Other Knight Boys: Jane Austen’s Dispossessed Nephews. If you have been following my blog Reading with Austen: Returning the Lost Sheep of Godmersham, you have seen the several posts on the diaries of Charles Bridges Knight, i.e all the excerpts that Hazel shared with me of Charles’ references to his reading in the library at Godmersham Park, home to his father, and Jane Austen’s brother, Edward Austen Knight [see below for links to these posts]. Hazel has been researching not only the life of Charles, but also the lives of the five other sons of Edward [all six in order are: Edward, George, Henry, William, Charles, and John]. Her recently published book just flows with tales of their childhood into manhood adventures. I highly recommend it, many of the stories worthy of an Austen novel!
So, Welcome Hazel!
JAIV: Can you give a brief summary of the book?
HJ: Jane Austen’s letters provide clear-sighted glimpses of her six Knight nephews as they grew up, but hers was not the only pen to record their privileged upbringing. Cassandra and Henry Austen commented on Edward Austen Knight’s indulgence of his sons and worried about the boys’ ability to cope with future adversity in the wider world; their affectionate sister Fanny noted key moments in their lives – birthdays, holidays, marriages; Charles kept a detailed diary throughout the 1830s and 40s. The Other Knight Boys explores the character of each nephew in turn, their professional and personal circumstances, their close fraternal bonds as well as the difficulties and disappointments they encountered in adulthood. For five of the brothers, future dispossession of their beloved family home at Godmersham as a consequence of birth order was a reality they had to live with. How it affected the choices they made forms the story that the book attempts to tell.
JAIV: How did you end up doing this research on Austen’s nephews, the six sons of her brother Edward?
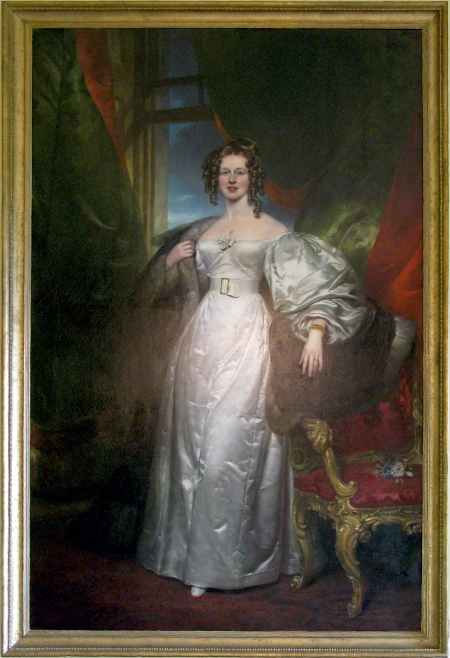
HJ: Quite by chance, in 2010, I was in a small party on a guided tour of Trafalgar (pronounced Traffle-gar) Park near Salisbury in Wiltshire. The property featured as Hartfield in the 1996 ITV film of Emma [with Kate Beckinsale], as well as Barton Park in Emma Thompson’s Sense & Sensibility. Originally known as Standlynch Park, it was acquired in 1813 by Parliament for Nelson’s brother William, the new 1st Earl Nelson and re-named Trafalgar Park. The Nelson family lived here until 1946. In 2010, the owner was Michael Wade, whose housekeeper conducted us around the ground floor rooms. In the saloon she pointed out a stunning full length portrait of William Nelson’s beautiful wife, Hilare. Wait a minute, I thought, wasn’t she subsequently married to one of Jane Austen’s Knight nephews? Next followed some very intensive sleuthing which uncovered baptismal records in Cornwall and three marriages – to a cousin, to Nelson and eventually to George Knight of Godmersham. The Kent History and Library Centre and the British Library supplied more biographical material and in a room not usually open to visitors at Chawton House, I found a portrait of George as a young man. My research turned into an article on the couple for the 2016 Jane Austen Society Annual Report. After that came the urge to write about the other five Knight boys and uncover as much as possible about the women in their lives. Charles of course never married, but he had close relationships with his father, his brothers and their spouses.
[Portrait of Hilare Countess Nelson, by George Sanders, 1829-34. Courtesy of Martyn Downer and Michael Wade]
JAIV: Your research took you to materials scattered throughout southern England – “Kent, Hampshire, and beyond” as you say (3). Was most of this known or did you discover any untapped sources?
HJ: The archives in Hampshire Record Office and the Kent Archives at Maidstone have been scoured pretty thoroughly by Austen scholars across many generations, although even here I discovered one or two sparkling gems which had never appeared in any other text. Previously ‘untapped sources’ for me were the Winchester College Archives, the matriculation records held at St John’s and University College in Oxford, the Nelson archive at the British Library and the War Office records at the National Archive, Kew. Articles in the Jane Austen Society Annual Reports (now accessible online) also filled in a number of gaps and put me in touch with other Austen / Knight researchers such as Margaret Wilson, who then provided material I would not otherwise have found. Sophia Hillan, Linda Slothouber, Maggie Lane and Deirdre Le Faye were also happy to have their generous flow of scholarship ‘tapped’. Karen ievers, Andrew Bradford and Hampshire Cultural Trust allowed me to see and reproduce previously unseen images.
JAIV: Of the six boys-to-men you researched, was there more information available from sources on any one more than others? And if so, was that frustrating? For instance I know that Charles kept extensive diaries for years – did any of the others leave such behind them?
HJ: Edward’s life is well documented, given that he was the eldest son and lived at Chawton House, but there are few examples, beyond business letters, of his own personal voice. George’s facility with language shines through his amusing poems and articles on cricket written for The Sporting Magazine. His restless character is evidenced by Fanny’s reports of his comings and goings between England and the Continent, his inability to settle to a career in the law and Charles’s revelation of his brother’s wish to try his luck in America. Letters were written to Fanny by all of the brothers, she records their arrival in her daily diary entries, but where are they now? I wish I had found a greater number of letters from Henry to Lizzy Rice. He comes across as the most contentedly independent and self-sufficient of all the brothers; the harrowing nature of his early death tugs at my heart strings. One or two of William’s letters have survived, together with contemporary descriptions of his youthful exuberance and Fanny’s revelation of his affair with the Knatchbull governess. John is the brother about whom least is known and the hardest to pin down on the page, yet his moving account of the loss of Godmersham is the most revealing of all.
JAIV: Edward, of course, was the heir, and while he appears to have maintained a close and friendly relationship with each of his brothers, there had to have been some bad feelings about how he really dispossessed all of them from their Godmersham Park home. Do you feel sympathetic toward him? Did he have any choice?
HJ: Edward’s siblings must have understood that maintaining Chawton House and Godmersham Park was impossible. The drain of his first and second families on Edward’s finances would have been excessive. The sons from his first marriage were at the stage where they required cash, so when Edward Austen Knight died, money came their way via their father. What appears inexplicable is Edward’s expensive and architecturally unsympathetic alterations to Godmersham in 1853, shortly before he decided to lease the property for 20 years. I can understand his attachment to Chawton – it had been his permanent home since 1826, although his frequent and lengthy returns to Kent each year might have misled his brothers and sisters into believing he would eventually move back and continue to make Godmersham available to all the family. When he sold it in 1875, of the brothers only John was still alive.
JAIV: Some great drama in the family! What is your favorite story? [then I’ll tell you mine!]
HJ: Difficult to choose one … Louisa Lushington’s* description on her visit to Godmersham of the boys somersaulting into the river fully clothed comes near the top of the list and I rather like the story Henry and George concocted, featuring Uncle Henry Austen’s imprisonment for poisoning his second wife. Scandal is always irresistible too … Fanny’s snide references to Fanny Jones, the consequences of Edward’s elopement with Mary Dorothea, William’s affair with the governess.
*[The Journal of Louisa Lushington (1821-22), with an introduction by Linda Slothouber, Chawton House, 2017]
Ok, so you mention my favorite! Edward’s elopement with his sister’s step-daughter is quite compelling, and definitely worthy of a novel – I cannot tell anymore, readers – buy the book!
Photograph of a lost portrait of Edward Knight,
held by Kent County Cricket Club, Canterbury.
JAIV: There was so much tragedy in their lives: not unlike their father and uncles (excepting the youngest John, and Charles who never married), all suffered the loss of first wives in childbirth or illness. It is really wrenching to read – how do you think they all handled this?
HJ: Tragedies such as these are almost unimaginable in our modern age of effective remedies, reliable diagnoses and informed medical expertise. Death in childbirth happened so frequently that many women – judging by their correspondence – did not expect to survive, so perhaps their husbands anticipated the worst before it happened. As for the Knight husbands, they certainly grieved for a time, it’s difficult to tell for how long, but from Charles’s diaries we learn that Edward was decimated by the loss of Mary Dorothea and that William and Henry were emotionally affected on the first anniversary of their wives’ deaths. Two or three years later, they are all married again, and embarking on the creation of second families. Life went on. Perhaps a combination of strong religious belief, practical rationality and fraternal support carried them through the worst.

Elizabeth Bridges Knight – Jane Austen blog by Kleurrijk
JAIV: Any sense that the death of their mother after the birth of her 11th child (Brook John, known as John) in 1808 (Edward was 14) had a long-lasting effect on any/each of them?
HJ: John would not have remembered his mother and Charles’s recollections were probably indistinct at best. The affection the brothers felt for each other, for their sisters, and for their father – and his for them – strengthened the familial tie after Elizabeth’s death. Their easy, happy life at Godmersham appears to continue much the same as before, with Fanny standing in as a very capable and loving presence. Male and female occupations and interests were largely separate and distinct, which perhaps helped to lessen the sense of loss at the time and later. Edward, George, Henry and William were away at school for most of the year, Charles and John were initially under Fanny’s care until the time came for them to leave. Any long term effect might have manifested itself in a very understandable anxiety when their own wives became pregnant.
JAIV: Was Jane Austen a big factor in any of their lives growing up (she died when Edward was 23 in July 1817)? But when she became more popular and James Edward Austen Leigh (James’s son) wrote her memoir in 1869 – did any of Edward’s children contribute to that?
HJ: According to Anna Lefroy, Jane Austen was not loved by the Knight children, although they appreciated her story-telling skills. Anna had her own reasons for holding this view, but the probability is that Jane was merely tolerated by the nephews while at Godmersham, especially as they grew older and beyond female influence. Given their hunting, fishing and shooting pursuits, Jane called it ‘sporting mania’, they would see little of her during the day and there is evidence that at and after dinner, she found their their male acquaintance and their talk of wholesale slaughter distasteful. Maria Bertram, bored silly by Mr Rushworth’s boast of game bagged and poachers apprehended, comes to mind. A spinster aunt casting disapproving looks across the table, however, would have had little effect on these confident, indulged young men. At Chawton, out of the hunting season, the nephews appear to have proved more congenial company, especially Henry and William, whose visits to the Cottage in their aunt’s final year are recorded with great affection in her letters. In 1822, Henry Knight wrote to his sister Lizzy that he expected Chawton to feel ‘sadly unreal’, surely on account of Aunt Jane’s absence, when he next visited.
James Edward Austen-Leigh attempted to access Fanny’s letters from Jane Austen, but did not succeed. He stayed with William Knight at the new Steventon Rectory for a day and night, in order to walk the familiar lanes and remind himself of where the old rectory used to stand. At the time the Memoir was written, Henry, George and Charles were dead.
JAIV: In reading about Edward’s family, do you feel that at any time in her writing that Jane Austen was modelling a character after a real-life family member?
HJ: No. [ha! Love this very succinct answer!]
JAIV: What surprised you the most? – Something previously unknown to you or anyone else in the Austen research world?
HJ: A small discovery involved Henry’s attendance at University College, Oxford. There is no reference to this in other texts and it was even a surprise to Deirdre Le Faye. Another concerns George’s final years, after his wife’s death. I am intrigued by his relationship, whatever it entailed, with Fanny Jones. George’s sister Lady Knatchbull certainly suspected something untoward, especially when her brother moved to Hereford to share a house with Fanny and her husband. One that almost got away is the small sheet of paper, Plate 8 in my book, comprising poems written by Edward Knight II and his second wife Adela. It was listed in the HRO catalogue, but missing from the file. It had still not surfaced when my last day at the Record Office came, but in the three hours it took to drive home, the Archivist had located, photocopied and forwarded it.
JAIV: For instance, Charles went to Cambridge not Oxford like the rest of his family – do you know why that was?
HJ: One of my theories is that he was sent to Cambridge to detach him from certain school friends who had involved him in a rebellion at Winchester College in 1818. A number of the expelled ringleaders went on to Oxford, with which Winchester was closely associated. His sister Fanny reveals that Charles was ‘intended for the Law’ at this point – maybe Cambridge had a better reputation for training lawyers. One can only speculate.
JAIV: All the brothers had very interesting and novel-worthy love interests – some thwarted by parental involvement – but there were elopements, governess shenanigans, some intermarriage with cousins, etc., some of which you have mentioned above – Charles was the only brother not to marry – was there any love interest found in his diaries?
HJ: From time to time, Charles expresses a lukewarm interest in what he calls ‘domestic happiness’ but he recognized at the same time that it would very likely result in a diminution of his income and the luxury it afforded. While living at Godmersham he attended balls with his sisters, usually reporting afterwards that he had found them ‘stupid’ or that he ‘had not been up to the mark’. He is open to the appeal of women and notes their beauty, or lack of it, and liveliness. In the summer of 1847, when Charles was forty-four, heavily inked deletions appear in his diaries, which appear to be linked to Lizzie Pole, a young woman he encountered at Wolverton Rectory. That Charles himself was not responsible for these obliterations is a possibility, since not all of the references to ‘dear Lizzie’ are removed. His end of the year summary for 1847 expresses ‘shame and sorrow’ at his unbecoming behaviour and ‘cold unfeeling heart’. What happened remains a mystery.
JAIV: Charles’ diaries are quite detailed and extensive. Are you hoping to do more with them? Make them available to a larger audience? [You were terrific in sharing excerpts from the diaries about Charles’ reading while at Godmersham – see links below]
HJ: Yes indeed. See the answer below!
JAIV: Your previous books, Jane Austen and Marriage (2009, paperback 2017 by Uppercross Press), Jane Austen’s Journeys (2014) are both excellent and informative reads where you discuss the times Jane Austen lived in and how the understanding of that helps us understand her plots and characters. Did you enjoy researching the real people in Austen’s life more or less than delving into a subject?
HJ: I loved creating both of my previous books, but have found biographical writing fascinating and wholly compelling (for that, read obsessive). The Other Knight Boys was my first foray as a writer into this territory and I must admit I did find this kind of study more absorbing than focusing on a set subject. It’s something of a cliché to say it, but I did develop a strong sense of each nephew as a living breathing individual, and consequently able to make informed leaps into speculative musing where there were gaps in the records. Where the boys’ experiences overlapped – attendance at Henry and Sophia’s wedding, for example, or the visit to Ireland on their sister Cassandra’s death – deciding in which chapter or chapters to locate the material and at the same time avoiding unnecessary repetition, was a very complex but rewarding process, rather like solving a six-dimensional puzzle.
JAIV: Which leads us to: What’s up next?
HJ: I am currently working with Peter Sabor on the transcription and annotation of Charles Knight’s diaries – 1832 – 1851.
[The Sophia Hillan book May, Lou & Cass: Jane Austen’s Nieces in Ireland (Blackstaff Press, 2011) covers the lives of Marianne (May), Louisa, and Cassandra Jane – much has already been written about Fanny, so what about Elizabeth (Lizzy) – is there a story to tell there?
M.C. Hammond’s Relating to Jane has already covered Lizzy Rice’s life.
[JAIV: Goodness, I have this book on my shelf and have never read it – more than half the book is on Lizzy Knight!: Relating to Jane: Studies on the Life and Novels of Jane Austen with a Life of Her Niece Elizabeth Austen/Knight, by M. C. Hammond (Minerva Press, 1998)].
JAIV: What is your favorite Austen and why? Your favorite character?
HJ: This reminds me of that question from a famous BBC Radio 4 programme: ‘Which book would you choose to take with you to your desert island?’ My answer would have to be ‘The Complete Works of Jane Austen’. I find it impossible to single out for special notice one novel or one character. Heroines, heroes and minor characters, they are all perfectly realized and crafted.
JAIV: An absolutely perfect answer! So, what else do you like to read?
HJ: I love reading biographies, by Claire Tomalin and Hermione Lee in particular, also intelligent detective and thriller fiction – P.D. James, Ian Rankin, Stella Rimington, Henning Mankell, Stieg Larsson, Kate Atkinson; authors from other genres include Dorothy Whipple, Hilary Mantel, C.J. Sansom, Tracey Chevalier … I could go on.
JAIV: well. Thank you for that – a perfect reading list to add to my already toppling TBR pile! [and I see that many of Dorothy Whipple’s books have been republished by the incomparable Persephone Books.]
****************
A hearty Thank You! Hazel, for sharing so much about your book and research into the world of Austen’s nephews. You give a very loving picture of their varied lives, emphasizing their continued connection and affection for each other, and giving us a compelling view into this next generation of the Austen family. The amount of your research alone astounds me! And again, I highly recommend it to all. If you have any questions for Hazel, please comment below and I will forward them to her for answering.
About the author:
Hazel Jones taught English at Exeter University’s Department of Lifelong Learning. She has lectured to Austen Societies in the UK, USA, Canada, Australia, and the Netherlands and contributed articles to a number of their journals. Since 1995 she has tutored residential courses on Jane Austen’s life, letters and novels in a range of locations. Her published books include Jane Austen and Marriage (2009) and Jane Austen’s Journeys (2014).
The Other Knight Boys: Jane Austen’s Dispossessed Nephews, by Hazel Jones
Crediton, Devon, UK: Uppercross Press, 2020.
165 pages, color illustrations, notes, bibliography, index.
You can find Hazel’s book at:
- Chawton House online bookshop: https://chawtonhouse.org/shop/books/the-other-knight-boys-hazel-jones/
- Jane Austen’s House – currently closed due to COVID-19, but call: https://janeaustens.house/
- P&G Wells in Winchester: https://www.bookwells.co.uk/
- Jane Austen Books in the USA: https://www.janeaustenbooks.net/search?type=product,article,page&q=*other%20knight%20boys*
***********
The blog posts on Charles Bridges Knight’s reading at Godmersham Park can be found here:














 [CHL book with bookplate and shelf ticket]
[CHL book with bookplate and shelf ticket]













































































